So, now that you are weaving overshot on your loom, what exactly is overshot? Where did it come from? What makes it so cool?
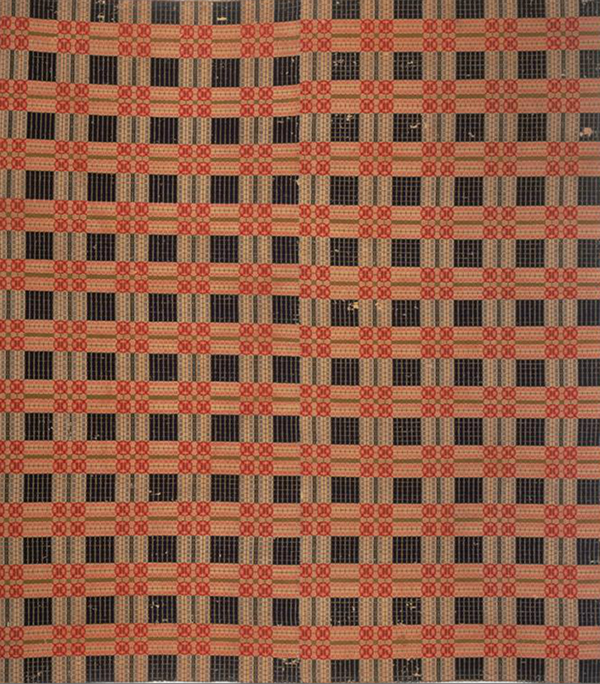
The origin of the technique itself may have started in Persia and spread to other parts of the world, according to the author, Hans E. Wulff, of The Traditional Crafts of Persia. However, it is all relatively obscured by history. In The Key to Weaving by Mary E. Black, she mentioned that one weaver, who was unable to find a legitimate definition of the technique thought that the name “overshot” was a derivative of the idea that “the last thread of one pattern block overshoots the first thread of the next pattern block.” I personally think it is because the pattern weft overshoots the ground warp and weft webbing.

Overshot gained popularity and a place in history during the turn of the 19th century in North America for coverlets. Coverlets are woven bedcovers, often placed as the topmost covering on the bed. A quote that I feel strengthens the craftsmanship and labor that goes into weaving an overshot coverlet is from The National Museum of the American Coverlet:
“A quilt is generally assembled from pre-existing cloth. A coverlet is made from scratch.”
Though, popular in many states during the early to mid 19th centuries, the extensive development of overshot weaving as a form of design and expression was fostered in rural southern Appalachia. It remained a staple of hand-weavers in the region until the early 20th century. In New England, around 1875, the invention of the Jacquard loom, the success of chemical dyes and the evolution of creating milled yarns, changed the look of coverlets entirely. The designs woven in New England textile mills were predominantly pictorial and curvilinear. So, while the weavers of New England set down their shuttles in favor of complex imagery in their textiles, the weavers of Southern Appalachia continued to weave for at least another hundred years using single strand, hand spun, irregular wool yarn that was dyed with vegetable matter, by choice.

Designs were focused on repeating geometric patterns that were created by using a supplementary weft that was typically a dyed woolen yarn over a cotton plain weave background. The designs expressed were often handed down through family members and shared within communities like a good recipe. And each weaver was able to develop their own voice by adjusting the color ways and the treadling arrangements. Predominately, the homestead weavers that gave life and variations to these feats of excellent craftsmanship were women. However, not every home could afford a loom, so the yarn that was spun would have been sent out to be woven by the professional weavers, who were mostly men.
And, due to the nature of design, overshot can be woven on simpler four harness looms. This was a means for many weavers to explore this technique who may not have the financial means to a more complicated loom. With this type of patterning a blanket could be woven in narrower strips and then hand sewn together to cover larger beds. This allowed weavers to create complex patterns that spanned the entirety of the bed.
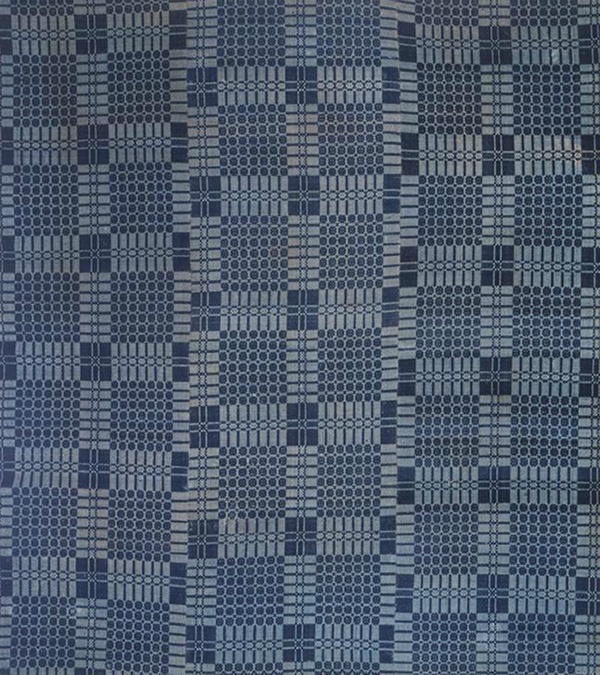
What makes overshot so incredibly interesting that it was fundamentally a development of American weavers looking to express themselves. Many of the traditional patterns have mysterious names such as “Maltese Cross”, “Liley of the West”, “Blooming Leaf of Mexico” and “Lee’s Surrender”. Although the names are curious, the patterns that were developed from the variations of four simple blocks are incredibly intricate and luxurious.
This is only the tip of the iceberg with regard to the history of this woven structure. If you are interested in learning more about the culture and meaning of overshot, check out these resources!
The National Museum of the American Coverlet- a museum located in Bedford, Pennsylvania that has an extensive collection of traditional and jacquard overshot coverlets. Great information online and they have a “Coverlet College” which is a weekend series of lectures to learn everything about the American coverlet. Check out their website - coverletmuseum.org
Textile Art of Southern Appalachia: The Quiet Work of Women – This was an exhibit that traveled from Lowell, Massachusetts, Morehead, Kentucky, Knoxville, Tennessee, Raleigh, North Carolina, and ended at the Royal Museum in Edinburgh, Scotland. The exhibit contained a large number of overshot coverlets and the personal histories of those who wove them. I learned of this exhibit through an article written by Kathryn Liebowitz for the 2001, June/July edition of the magazine “Art New England”. The book that accompanied the exhibit, written by Kathleen Curtis Wilson, contains some of the rich history of these weavers and the cloth they created. I have not personally read the book, but it is now on the top of my wish list, so when I do, you will be the first to know about it! The book is called Textile Art of Southern Appalachia: The Quiet Work of Women and I look forward to reading it.
And my own collection of books that I pulled together information from:
- The Key to Weaving: A textbook of hand weaving for the beginning weaver by Mary E. Black
- Mastering Weave Structures by Sharon Alderman
And the book that got me fascinated with overshot in the first place, A Handweaver’s Pattern Book by Marguerite P. Davison.
Do you love overshot as well? Tell me what you know about it! I would also love to see what patterns you have woven yourself.
Images were sourced from ARTstor, a digital library of images from the arts, architecture, humanities, and sciences.
Felipe
Tegan Frisino
Debra Anderson
Tegan Frisino
Debra Anderson
Debra Anderson
Tegan Frisino
Debra Anderson
Tegan Frisino
Debbie
Tegan Frisino
Neil Colmer
Neil Colmer
Carol-Ann Apilado
Tegan Frisino
Mara Montelibano
Ann